Fallen Arches Causes And Treatment
Overview
Fallen arches, or flatfoot, is a condition in which the arch on the inside of the foot is flat and the entire sole of the foot rests on the ground. It affects about 40% of the general population. Although flat feet in themselves are not usually problematic, they can create problems in the feet, hips, ankles and knees. Pain may be experienced in the lower back if there are alignment problems and if the individual is engaged in a lot of heavy, high impact activities that put stress on the bones and muscles in the lower legs. The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Causes
Some people develop fallen arches because they tend to pronate, or roll inwards on the ankles, says the Instep Foot Clinic. Other people may simply have under-developed muscles in their arches. Your arches help your feet bear weight and are supported in this job by muscles and tendons in your feet and ankles. So, while fallen arches aren?t usually serious, they can cause pain in your feet, ankles, knees and/or hips due to your reduced weight-bearing ability. In these cases, treatment may be required. Orthotics that sit in your shoes and support your arches are a common solution, as are exercises to strengthen and stretch your feet and leg muscles.
Symptoms
Some people have fallen arches, and they aren?t even aware of it, fallen arches are sometimes asymptomatic and do not always cause pain. However, for others, the following symptoms may be present. Foot pain, particularly in the arches or heels, leg or back pain, feet feel tired quickly, swelling in the feet and difficulty moving the feet.
Diagnosis
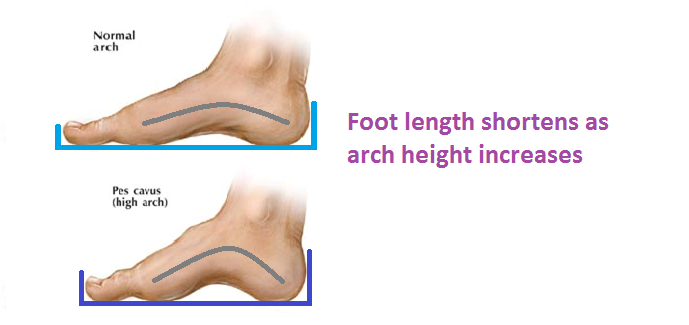
There are a few simple ways to assess your foot type, and most include making an imprint of your footprint. The classic way is to stand on a hard floor surface with wet feet to make a wet foot print. Look at the narrowest part of your footprint, which should be between your heel and ball of your foot. If the print of your foot in this part is less than 10% of the width of the widest part then you are likely to have high arches. more than 10% but less than 25% then your foot profile is probably normal, more than 25% or even the widest part, then you have flat feet.
Is flat footedness genetic?
Non Surgical Treatment
Most cases of fallen arches are not painful and need no form of treatment. However, common symptoms of fallen arches can include pain in your feet (particularly in the area of your heel or arch), pain in your feet that persists after long bouts of physical activity or standing up, achy feet, or arch pain when standing on the tips of your toes. Most cases of fallen arches are not preventable. Treatments for fallen arches include, rest, ice, compression, medication to relieve pain, orthotics, or in some cases surgery.
Surgical Treatment
Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.
Fallen arches, or flatfoot, is a condition in which the arch on the inside of the foot is flat and the entire sole of the foot rests on the ground. It affects about 40% of the general population. Although flat feet in themselves are not usually problematic, they can create problems in the feet, hips, ankles and knees. Pain may be experienced in the lower back if there are alignment problems and if the individual is engaged in a lot of heavy, high impact activities that put stress on the bones and muscles in the lower legs. The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Causes
Some people develop fallen arches because they tend to pronate, or roll inwards on the ankles, says the Instep Foot Clinic. Other people may simply have under-developed muscles in their arches. Your arches help your feet bear weight and are supported in this job by muscles and tendons in your feet and ankles. So, while fallen arches aren?t usually serious, they can cause pain in your feet, ankles, knees and/or hips due to your reduced weight-bearing ability. In these cases, treatment may be required. Orthotics that sit in your shoes and support your arches are a common solution, as are exercises to strengthen and stretch your feet and leg muscles.
Symptoms
Some people have fallen arches, and they aren?t even aware of it, fallen arches are sometimes asymptomatic and do not always cause pain. However, for others, the following symptoms may be present. Foot pain, particularly in the arches or heels, leg or back pain, feet feel tired quickly, swelling in the feet and difficulty moving the feet.
Diagnosis
There are a few simple ways to assess your foot type, and most include making an imprint of your footprint. The classic way is to stand on a hard floor surface with wet feet to make a wet foot print. Look at the narrowest part of your footprint, which should be between your heel and ball of your foot. If the print of your foot in this part is less than 10% of the width of the widest part then you are likely to have high arches. more than 10% but less than 25% then your foot profile is probably normal, more than 25% or even the widest part, then you have flat feet.
Is flat footedness genetic?
Non Surgical Treatment
Most cases of fallen arches are not painful and need no form of treatment. However, common symptoms of fallen arches can include pain in your feet (particularly in the area of your heel or arch), pain in your feet that persists after long bouts of physical activity or standing up, achy feet, or arch pain when standing on the tips of your toes. Most cases of fallen arches are not preventable. Treatments for fallen arches include, rest, ice, compression, medication to relieve pain, orthotics, or in some cases surgery.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.