Fallen Arches Causes And Treatment
Overview
Fallen arches, or flatfoot, is a condition in which the arch on the inside of the foot is flat and the entire sole of the foot rests on the ground. It affects about 40% of the general population. Although flat feet in themselves are not usually problematic, they can create problems in the feet, hips, ankles and knees. Pain may be experienced in the lower back if there are alignment problems and if the individual is engaged in a lot of heavy, high impact activities that put stress on the bones and muscles in the lower legs. The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Causes
Some people develop fallen arches because they tend to pronate, or roll inwards on the ankles, says the Instep Foot Clinic. Other people may simply have under-developed muscles in their arches. Your arches help your feet bear weight and are supported in this job by muscles and tendons in your feet and ankles. So, while fallen arches aren?t usually serious, they can cause pain in your feet, ankles, knees and/or hips due to your reduced weight-bearing ability. In these cases, treatment may be required. Orthotics that sit in your shoes and support your arches are a common solution, as are exercises to strengthen and stretch your feet and leg muscles.
Symptoms
Some people have fallen arches, and they aren?t even aware of it, fallen arches are sometimes asymptomatic and do not always cause pain. However, for others, the following symptoms may be present. Foot pain, particularly in the arches or heels, leg or back pain, feet feel tired quickly, swelling in the feet and difficulty moving the feet.
Diagnosis
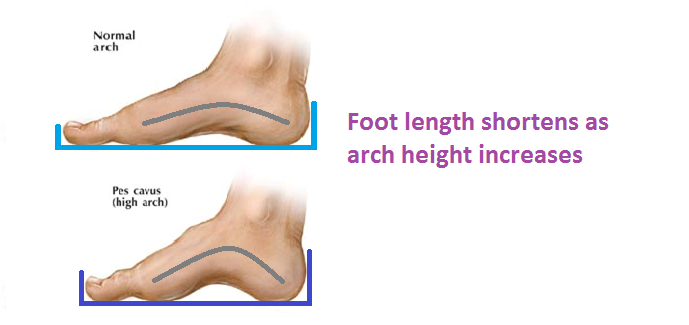
There are a few simple ways to assess your foot type, and most include making an imprint of your footprint. The classic way is to stand on a hard floor surface with wet feet to make a wet foot print. Look at the narrowest part of your footprint, which should be between your heel and ball of your foot. If the print of your foot in this part is less than 10% of the width of the widest part then you are likely to have high arches. more than 10% but less than 25% then your foot profile is probably normal, more than 25% or even the widest part, then you have flat feet.
Is flat footedness genetic?
Non Surgical Treatment
Most cases of fallen arches are not painful and need no form of treatment. However, common symptoms of fallen arches can include pain in your feet (particularly in the area of your heel or arch), pain in your feet that persists after long bouts of physical activity or standing up, achy feet, or arch pain when standing on the tips of your toes. Most cases of fallen arches are not preventable. Treatments for fallen arches include, rest, ice, compression, medication to relieve pain, orthotics, or in some cases surgery.
Surgical Treatment
Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.
Fallen arches, or flatfoot, is a condition in which the arch on the inside of the foot is flat and the entire sole of the foot rests on the ground. It affects about 40% of the general population. Although flat feet in themselves are not usually problematic, they can create problems in the feet, hips, ankles and knees. Pain may be experienced in the lower back if there are alignment problems and if the individual is engaged in a lot of heavy, high impact activities that put stress on the bones and muscles in the lower legs. The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Causes
Some people develop fallen arches because they tend to pronate, or roll inwards on the ankles, says the Instep Foot Clinic. Other people may simply have under-developed muscles in their arches. Your arches help your feet bear weight and are supported in this job by muscles and tendons in your feet and ankles. So, while fallen arches aren?t usually serious, they can cause pain in your feet, ankles, knees and/or hips due to your reduced weight-bearing ability. In these cases, treatment may be required. Orthotics that sit in your shoes and support your arches are a common solution, as are exercises to strengthen and stretch your feet and leg muscles.
Symptoms
Some people have fallen arches, and they aren?t even aware of it, fallen arches are sometimes asymptomatic and do not always cause pain. However, for others, the following symptoms may be present. Foot pain, particularly in the arches or heels, leg or back pain, feet feel tired quickly, swelling in the feet and difficulty moving the feet.
Diagnosis
There are a few simple ways to assess your foot type, and most include making an imprint of your footprint. The classic way is to stand on a hard floor surface with wet feet to make a wet foot print. Look at the narrowest part of your footprint, which should be between your heel and ball of your foot. If the print of your foot in this part is less than 10% of the width of the widest part then you are likely to have high arches. more than 10% but less than 25% then your foot profile is probably normal, more than 25% or even the widest part, then you have flat feet.
Is flat footedness genetic?
Non Surgical Treatment
Most cases of fallen arches are not painful and need no form of treatment. However, common symptoms of fallen arches can include pain in your feet (particularly in the area of your heel or arch), pain in your feet that persists after long bouts of physical activity or standing up, achy feet, or arch pain when standing on the tips of your toes. Most cases of fallen arches are not preventable. Treatments for fallen arches include, rest, ice, compression, medication to relieve pain, orthotics, or in some cases surgery.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.
Leg Length Discrepancy Right After Total Hip Arthroplasty
Overview
Some people have an ?apparent? LLD which may make the affected leg seem longer than the other leg. There are several factors that can contribute to this feeling. Most commonly, contractures or shortening of the muscles surrounding the hip joint and pelvis make the involved leg feel longer, even when both legs are really the same length. Additionally, contractures of the muscles around the lower back from spinal disorders (i.e. arthritis, spinal stenosis), curvatures of the spine from scoliosis, and deformities of the knee or ankle joint can make one leg seem longer or shorter. In the general public, some people have an ?apparent LLD? as long as one half inch but usually don?t notice it because the LLD occurs over time. A ?true? LLD is where one leg is actually longer than the other. Patients can have unequal leg lengths of 1/4? to 1/2? and never feel it too! You can also have combinations of ?True? and ?Apparent? LLDs. During total hip replacement surgery, the surgeon may ?lengthen? the involved leg by stretching the muscles and ligaments that were contracted, as well as by restoring the joint space that had become narrowed from the arthritis. This is usually a necessary part of the surgery because it also provides stability to the new hip joint. Your surgeon takes measurements of your leg lengths on x-ray prior to surgery. Your surgeon always aims for equal leg lengths if at all possible and measures the length of your legs before and during surgery in order to achieve this goal. Occasionally, surgeons may need to lengthen the operable leg to help improve stability and prevent dislocations as well improve the muscle function around the hip.
Causes
A number of causes may lead to leg length discrepancy in children. Differences in leg length frequently follow fractures in the lower extremities in children due to over or under stimulation of the growth plates in the broken leg. Leg length discrepancy may also be caused by a congenital abnormality associated with a condition called hemihypertrophy. Or it may result from neuromuscular diseases such as polio and cerebral palsy. Many times, no cause can be identified. A small leg length discrepancy of a quarter of an inch or less is quite common in the general population and of no clinical significance. Larger leg length discrepancies become more significant. The long-term consequences of a short leg may include knee pain, back pain, and abnormal gait or limp.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
The doctor carefully examines the child. He or she checks to be sure the legs are actually different lengths. This is because problems with the hip (such as a loose joint) or back (scoliosis) can make the child appear to have one shorter leg, even though the legs are the same length. An X-ray of the child?s legs is taken. During the X-ray, a long ruler is put in the image so an accurate measurement of each leg bone can be taken. If an underlying cause of the discrepancy is suspected, tests are done to rule it out.
Non Surgical Treatment
In an adult, we find that we can add a non compressive silicone heel lift to a shoe in increments of 3-4 mm maximum per week. Were we to give a patient with a 20 mm short leg, 20 mm of lift all at once, their entire body would rebel. The various compensations that the body has made, such as curvatures and shortening of muscles on the convex side of the curve, would make such a dramatic change not just noticeable, but painful. When we get close to balancing a patient by lifting a leg with heel inserts, then we perform another gait analysis and follow up xray. At that point, we can typically write them a final prescription to have their shoe modified. A heel lift is typically fine up to 7 mm. When it gets higher than that, the entire shoe must be modified. There are two reasons for this. The back of the shoe is generally too short to accommodate more than 7-8 mm inserted inside the shoes and a heel lift greater than 7 mm will lead to Achilles tendon shortening, which then creates it?s own panoply of problems.

heelsncleavage
Surgical Treatment
Surgical lengthening of the shorter extremity (upper or lower) is another treatment option. The bone is lengthened by surgically applying an external fixator to the extremity in the operating room. The external fixator, a scaffold-like frame, is connected to the bone with wires, pins or both. A small crack is made in the bone and tension is created by the frame when it is "distracted" by the patient or family member who turns an affixed dial several times daily. The lengthening process begins approximately five to ten days after surgery. The bone may lengthen one millimeter per day, or approximately one inch per month. Lengthening may be slower in adults overall and in a bone that has been previously injured or undergone prior surgery. Bones in patients with potential blood vessel abnormalities (i.e., cigarette smokers) may also lengthen more slowly. The external fixator is worn until the bone is strong enough to support the patient safely, approximately three months per inch of lengthening. This may vary, however, due to factors such as age, health, smoking, participation in rehabilitation, etc. Risks of this procedure include infection at the site of wires and pins, stiffness of the adjacent joints and slight over or under correction of the bone?s length. Lengthening requires regular follow up visits to the physician?s office, meticulous hygiene of the pins and wires, diligent adjustment of the frame several times daily and rehabilitation as prescribed by your physician.
Some people have an ?apparent? LLD which may make the affected leg seem longer than the other leg. There are several factors that can contribute to this feeling. Most commonly, contractures or shortening of the muscles surrounding the hip joint and pelvis make the involved leg feel longer, even when both legs are really the same length. Additionally, contractures of the muscles around the lower back from spinal disorders (i.e. arthritis, spinal stenosis), curvatures of the spine from scoliosis, and deformities of the knee or ankle joint can make one leg seem longer or shorter. In the general public, some people have an ?apparent LLD? as long as one half inch but usually don?t notice it because the LLD occurs over time. A ?true? LLD is where one leg is actually longer than the other. Patients can have unequal leg lengths of 1/4? to 1/2? and never feel it too! You can also have combinations of ?True? and ?Apparent? LLDs. During total hip replacement surgery, the surgeon may ?lengthen? the involved leg by stretching the muscles and ligaments that were contracted, as well as by restoring the joint space that had become narrowed from the arthritis. This is usually a necessary part of the surgery because it also provides stability to the new hip joint. Your surgeon takes measurements of your leg lengths on x-ray prior to surgery. Your surgeon always aims for equal leg lengths if at all possible and measures the length of your legs before and during surgery in order to achieve this goal. Occasionally, surgeons may need to lengthen the operable leg to help improve stability and prevent dislocations as well improve the muscle function around the hip.

Causes
A number of causes may lead to leg length discrepancy in children. Differences in leg length frequently follow fractures in the lower extremities in children due to over or under stimulation of the growth plates in the broken leg. Leg length discrepancy may also be caused by a congenital abnormality associated with a condition called hemihypertrophy. Or it may result from neuromuscular diseases such as polio and cerebral palsy. Many times, no cause can be identified. A small leg length discrepancy of a quarter of an inch or less is quite common in the general population and of no clinical significance. Larger leg length discrepancies become more significant. The long-term consequences of a short leg may include knee pain, back pain, and abnormal gait or limp.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
The doctor carefully examines the child. He or she checks to be sure the legs are actually different lengths. This is because problems with the hip (such as a loose joint) or back (scoliosis) can make the child appear to have one shorter leg, even though the legs are the same length. An X-ray of the child?s legs is taken. During the X-ray, a long ruler is put in the image so an accurate measurement of each leg bone can be taken. If an underlying cause of the discrepancy is suspected, tests are done to rule it out.
Non Surgical Treatment
In an adult, we find that we can add a non compressive silicone heel lift to a shoe in increments of 3-4 mm maximum per week. Were we to give a patient with a 20 mm short leg, 20 mm of lift all at once, their entire body would rebel. The various compensations that the body has made, such as curvatures and shortening of muscles on the convex side of the curve, would make such a dramatic change not just noticeable, but painful. When we get close to balancing a patient by lifting a leg with heel inserts, then we perform another gait analysis and follow up xray. At that point, we can typically write them a final prescription to have their shoe modified. A heel lift is typically fine up to 7 mm. When it gets higher than that, the entire shoe must be modified. There are two reasons for this. The back of the shoe is generally too short to accommodate more than 7-8 mm inserted inside the shoes and a heel lift greater than 7 mm will lead to Achilles tendon shortening, which then creates it?s own panoply of problems.

heelsncleavage
Surgical Treatment
Surgical lengthening of the shorter extremity (upper or lower) is another treatment option. The bone is lengthened by surgically applying an external fixator to the extremity in the operating room. The external fixator, a scaffold-like frame, is connected to the bone with wires, pins or both. A small crack is made in the bone and tension is created by the frame when it is "distracted" by the patient or family member who turns an affixed dial several times daily. The lengthening process begins approximately five to ten days after surgery. The bone may lengthen one millimeter per day, or approximately one inch per month. Lengthening may be slower in adults overall and in a bone that has been previously injured or undergone prior surgery. Bones in patients with potential blood vessel abnormalities (i.e., cigarette smokers) may also lengthen more slowly. The external fixator is worn until the bone is strong enough to support the patient safely, approximately three months per inch of lengthening. This may vary, however, due to factors such as age, health, smoking, participation in rehabilitation, etc. Risks of this procedure include infection at the site of wires and pins, stiffness of the adjacent joints and slight over or under correction of the bone?s length. Lengthening requires regular follow up visits to the physician?s office, meticulous hygiene of the pins and wires, diligent adjustment of the frame several times daily and rehabilitation as prescribed by your physician.
What Are The Major Causes Of Heel Painfulness
Overview

Heel pain accounts for one of the most common types of pain felt in the foot. Pain in the heel of the foot can be caused as a result of exercise, daily work routines or recreational activities. Some type of repetitive stress on the foot is often at the root of heel pain. The largest bone in the foot is the calcaneus, or heel bone. When we walk, the heel bone is usually the first part of the foot that hits the ground and is responsible for supporting much of the body's weight. This makes the heel of the foot prone to injury.
Causes
Achilles tendon rupture, the tendon of the heel cord behind the ankle is torn. Bone bruise. Bone cyst, a solitary fluid-filled cyst (cavity) in a bone. Gout, levels of uric acid in the blood rise until the level becomes excessive (hyperuricemia), causing urate crystals to build up around the joints. This causes inflammation and severe pain when a gout attack happens. Neuroma (Morton's neuroma) a swollen nerve in the ball of the foot, commonly between the base of the second and third toes. Osteomyelitis , osteomyelitis means infection of the bone or bone marrow; inflammation of the bone due to infection. Osteomyelitis sometimes occurs as a complication of injury or surgery. In some cases, the infection may get into bone tissue from the bloodstream. Patients with osteomyelitis typically experience deep pain and muscle spasms in the inflammation area, as well as fever. Peripheral neuropathy, neuropathy is a collection of disorders that occurs when nerves of the peripheral nervous system (the part of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord) are damaged. The condition is generally referred to as peripheral neuropathy, and it is most commonly due to damage to nerve axons. Neuropathy usually causes pain and numbness in the hands and feet. It can result from traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic disorders and exposure to toxins. One of the most common causes of neuropathy is diabetes. Problems with your gait, wrong posture when walking/running. Rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, sometimes referred to as rheumatoid disease, is a chronic (long lasting), progressive and disabling auto-immune disease condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints, the tissue around the joints, and other organs in the human body. Rheumatoid arthritis usually affects the joints in the hands and feet first, but any joint may become affected. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis commonly have stiff joints and feel generally unwell and tired.
Symptoms
Usually worse with the first few steps in the morning or at the initial point of activity. The latter usually gets better with continued activity (squeaky hinge analogy). Walking, running, sprinting, hill running and jumping will increase the pain. Often, the natural response is to walk on the outside of the foot - in supination - to lessen the stress on the plantar fascia - resulting in new problems.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment includes resting from the activities that caused the problem, doing certain stretching exercises, using pain medication and wearing open-back shoes. Your doctor may want you to use a 3/8" or 1/2" heel insert. Stretch your Achilles tendon by leaning forward against a wall with your foot flat on the floor and heel elevated with the insert. Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications for pain and swelling. Consider placing ice on the back of the heel to reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
At most 95% of heel pain can be treated without surgery. A very low percentage of people really need to have surgery on the heel. It is a biomechanical problem and it?s very imperative that you not only get evaluated, but receive care immediately. Having heel pain is like having a problem with your eyes; as you would get glasses to correct your eyes, you should look into orthotics to correct your foot. Orthotics are sort of like glasses for the feet. They correct and realign the foot to put them into neutral or normal position to really prevent heel pain, and many other foot issues. Whether it be bunions, hammertoes, neuromas, or even ankle instability, a custom orthotic is something worth considering.
heel pain exercises
Prevention

A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don't underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight.

Heel pain accounts for one of the most common types of pain felt in the foot. Pain in the heel of the foot can be caused as a result of exercise, daily work routines or recreational activities. Some type of repetitive stress on the foot is often at the root of heel pain. The largest bone in the foot is the calcaneus, or heel bone. When we walk, the heel bone is usually the first part of the foot that hits the ground and is responsible for supporting much of the body's weight. This makes the heel of the foot prone to injury.
Causes
Achilles tendon rupture, the tendon of the heel cord behind the ankle is torn. Bone bruise. Bone cyst, a solitary fluid-filled cyst (cavity) in a bone. Gout, levels of uric acid in the blood rise until the level becomes excessive (hyperuricemia), causing urate crystals to build up around the joints. This causes inflammation and severe pain when a gout attack happens. Neuroma (Morton's neuroma) a swollen nerve in the ball of the foot, commonly between the base of the second and third toes. Osteomyelitis , osteomyelitis means infection of the bone or bone marrow; inflammation of the bone due to infection. Osteomyelitis sometimes occurs as a complication of injury or surgery. In some cases, the infection may get into bone tissue from the bloodstream. Patients with osteomyelitis typically experience deep pain and muscle spasms in the inflammation area, as well as fever. Peripheral neuropathy, neuropathy is a collection of disorders that occurs when nerves of the peripheral nervous system (the part of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord) are damaged. The condition is generally referred to as peripheral neuropathy, and it is most commonly due to damage to nerve axons. Neuropathy usually causes pain and numbness in the hands and feet. It can result from traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic disorders and exposure to toxins. One of the most common causes of neuropathy is diabetes. Problems with your gait, wrong posture when walking/running. Rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, sometimes referred to as rheumatoid disease, is a chronic (long lasting), progressive and disabling auto-immune disease condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints, the tissue around the joints, and other organs in the human body. Rheumatoid arthritis usually affects the joints in the hands and feet first, but any joint may become affected. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis commonly have stiff joints and feel generally unwell and tired.
Symptoms
Usually worse with the first few steps in the morning or at the initial point of activity. The latter usually gets better with continued activity (squeaky hinge analogy). Walking, running, sprinting, hill running and jumping will increase the pain. Often, the natural response is to walk on the outside of the foot - in supination - to lessen the stress on the plantar fascia - resulting in new problems.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment includes resting from the activities that caused the problem, doing certain stretching exercises, using pain medication and wearing open-back shoes. Your doctor may want you to use a 3/8" or 1/2" heel insert. Stretch your Achilles tendon by leaning forward against a wall with your foot flat on the floor and heel elevated with the insert. Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications for pain and swelling. Consider placing ice on the back of the heel to reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
At most 95% of heel pain can be treated without surgery. A very low percentage of people really need to have surgery on the heel. It is a biomechanical problem and it?s very imperative that you not only get evaluated, but receive care immediately. Having heel pain is like having a problem with your eyes; as you would get glasses to correct your eyes, you should look into orthotics to correct your foot. Orthotics are sort of like glasses for the feet. They correct and realign the foot to put them into neutral or normal position to really prevent heel pain, and many other foot issues. Whether it be bunions, hammertoes, neuromas, or even ankle instability, a custom orthotic is something worth considering.
heel pain exercises
Prevention

A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don't underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight.
Mortons Neuroma Solutions
Overview
 A morton's neuroma (or an "inter-digital" neuroma) is found between the toes of the foot, most commonly the third and fourth toes. It can also occur between the metatarsal bones (the long bones in the forefoot). It is basically an entrapped nerve, which becomes inflamed due to constant irritation from the surrounding bony structures.
A morton's neuroma (or an "inter-digital" neuroma) is found between the toes of the foot, most commonly the third and fourth toes. It can also occur between the metatarsal bones (the long bones in the forefoot). It is basically an entrapped nerve, which becomes inflamed due to constant irritation from the surrounding bony structures.
Causes
Morton's Neuroma is a foot condition caused from an abnormal function of the foot that leads to bones squeezing a nerve usually between the 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads. Symptoms of Morton's Neuroma often occur during or after you have been placing significant pressure on the forefoot area, while walking, standing, jumping, or sprinting. This condition can also be caused by footwear selection. Footwear with pointed toes and/or high heels can often lead to a neuroma. Constricting shoes can pinch the nerve between the toes, causing discomfort and extreme pain.
Symptoms
Pain is usually increased by forefoot weight bearing activities (such as running), with narrow-fitting footwear, or with high heeled shoes. It is usually painful to firmly touch the affected region and, in chronic cases, pain and sometimes an audible click, may be heard when squeezing the foot and toes together with the hand. Often a localized area of swelling may be evident at the site of injury.
Diagnosis
Negative signs include no obvious deformities, erythema, signs of inflammation, or limitation of movement. Direct pressure between the metatarsal heads will replicate the symptoms, as will compression of the forefoot between the finger and thumb so as to compress the transverse arch of the foot. This is referred to as Mulder?s Sign. There are other causes of pain in the forefoot. Too often all forefoot pain is categorized as neuroma. Other conditions to consider are capsulitis, which is an inflammation of ligaments that surrounds two bones, at the level of the joint. In this case, it would be the ligaments that attach the phalanx (bone of the toe) to the metatarsal bone. Inflammation from this condition will put pressure on an otherwise healthy nerve and give neuroma-type symptoms. Additionally, an intermetatarsal bursitis between the third and fourth metatarsal bones will also give neuroma-type symptoms because it too puts pressure on the nerve. Freiberg's disease, which is an osteochondritis of the metatarsal head, causes pain on weight bearing or compression.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment options vary with the severity of each neuroma, and identifying the neuroma early in its development is important to avoid surgical correction. For simple, undeveloped neuromas, a pair of thick-soled shoes with a wide toe box is often adequate treatment to relieve symptoms, allowing the condition to diminish on its own. For more severe conditions, however, additional treatment or surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor. The primary goal of most early treatment regimens is to relieve pressure on areas where a neuroma develops. Your podiatric physician will examine and likely X-ray the affected area and suggest a treatment plan that best suits your individual case. Padding and Taping. Special padding at the ball of the foot may change the abnormal foot function and relieve the symptoms caused by the neuroma. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone injections can be prescribed to ease acute pain and inflammation caused by the neuroma. Orthotics. Custom shoe inserts made by your podiatrist may be useful in controlling foot function. Orthotics may reduce symptoms and prevent the worsening of the condition.
Surgical Treatment
If these non-surgical measures do not work, surgery is sometimes needed. Surgery normally involves a small incision (cut) being made on either the top, or the sole, of the foot between the affected toes. Usually, the surgeon will then either create more space around the affected nerve (known as nerve decompression) or will cut out (resect) the affected nerve. If the nerve is resected, there will be some permanent numbness of the skin between the affected toes. This does not usually cause any problems. You will usually have to wear a special shoe for a short time after surgery until the wound has healed and normal footwear can be used again. Surgery is usually successful. However, as with any surgical operation, there is a risk of complications. For example, after this operation a small number of people can develop a wound infection. Another complication may be long-term thickening of the skin (callus formation) on the sole of the foot (known as plantar keratosis). This may require treatment by a specialist in care of the feet (chiropody).
Prevention
Although the exact causes of neuromas are not completely known, the following preventive steps may help. Make sure your exercise shoes have enough room in the front part of the shoe and that your toes are not excessively compressed. Wear shoes with adequate padding in the ball of the foot. Avoid prolonged time in shoes with a narrow toe box or excessive heel height (greater than two inches).
 A morton's neuroma (or an "inter-digital" neuroma) is found between the toes of the foot, most commonly the third and fourth toes. It can also occur between the metatarsal bones (the long bones in the forefoot). It is basically an entrapped nerve, which becomes inflamed due to constant irritation from the surrounding bony structures.
A morton's neuroma (or an "inter-digital" neuroma) is found between the toes of the foot, most commonly the third and fourth toes. It can also occur between the metatarsal bones (the long bones in the forefoot). It is basically an entrapped nerve, which becomes inflamed due to constant irritation from the surrounding bony structures.Causes
Morton's Neuroma is a foot condition caused from an abnormal function of the foot that leads to bones squeezing a nerve usually between the 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads. Symptoms of Morton's Neuroma often occur during or after you have been placing significant pressure on the forefoot area, while walking, standing, jumping, or sprinting. This condition can also be caused by footwear selection. Footwear with pointed toes and/or high heels can often lead to a neuroma. Constricting shoes can pinch the nerve between the toes, causing discomfort and extreme pain.
Symptoms
Pain is usually increased by forefoot weight bearing activities (such as running), with narrow-fitting footwear, or with high heeled shoes. It is usually painful to firmly touch the affected region and, in chronic cases, pain and sometimes an audible click, may be heard when squeezing the foot and toes together with the hand. Often a localized area of swelling may be evident at the site of injury.
Diagnosis
Negative signs include no obvious deformities, erythema, signs of inflammation, or limitation of movement. Direct pressure between the metatarsal heads will replicate the symptoms, as will compression of the forefoot between the finger and thumb so as to compress the transverse arch of the foot. This is referred to as Mulder?s Sign. There are other causes of pain in the forefoot. Too often all forefoot pain is categorized as neuroma. Other conditions to consider are capsulitis, which is an inflammation of ligaments that surrounds two bones, at the level of the joint. In this case, it would be the ligaments that attach the phalanx (bone of the toe) to the metatarsal bone. Inflammation from this condition will put pressure on an otherwise healthy nerve and give neuroma-type symptoms. Additionally, an intermetatarsal bursitis between the third and fourth metatarsal bones will also give neuroma-type symptoms because it too puts pressure on the nerve. Freiberg's disease, which is an osteochondritis of the metatarsal head, causes pain on weight bearing or compression.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment options vary with the severity of each neuroma, and identifying the neuroma early in its development is important to avoid surgical correction. For simple, undeveloped neuromas, a pair of thick-soled shoes with a wide toe box is often adequate treatment to relieve symptoms, allowing the condition to diminish on its own. For more severe conditions, however, additional treatment or surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor. The primary goal of most early treatment regimens is to relieve pressure on areas where a neuroma develops. Your podiatric physician will examine and likely X-ray the affected area and suggest a treatment plan that best suits your individual case. Padding and Taping. Special padding at the ball of the foot may change the abnormal foot function and relieve the symptoms caused by the neuroma. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone injections can be prescribed to ease acute pain and inflammation caused by the neuroma. Orthotics. Custom shoe inserts made by your podiatrist may be useful in controlling foot function. Orthotics may reduce symptoms and prevent the worsening of the condition.

Surgical Treatment
If these non-surgical measures do not work, surgery is sometimes needed. Surgery normally involves a small incision (cut) being made on either the top, or the sole, of the foot between the affected toes. Usually, the surgeon will then either create more space around the affected nerve (known as nerve decompression) or will cut out (resect) the affected nerve. If the nerve is resected, there will be some permanent numbness of the skin between the affected toes. This does not usually cause any problems. You will usually have to wear a special shoe for a short time after surgery until the wound has healed and normal footwear can be used again. Surgery is usually successful. However, as with any surgical operation, there is a risk of complications. For example, after this operation a small number of people can develop a wound infection. Another complication may be long-term thickening of the skin (callus formation) on the sole of the foot (known as plantar keratosis). This may require treatment by a specialist in care of the feet (chiropody).
Prevention
Although the exact causes of neuromas are not completely known, the following preventive steps may help. Make sure your exercise shoes have enough room in the front part of the shoe and that your toes are not excessively compressed. Wear shoes with adequate padding in the ball of the foot. Avoid prolonged time in shoes with a narrow toe box or excessive heel height (greater than two inches).
Treating Leg Length Discrepancy With Shoe Lifts
There are not one but two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital implies that you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter compared to the other. As a result of developmental phases of aging, the brain picks up on the stride pattern and identifies some difference. The body typically adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch is not blatantly irregular, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and in most cases doesn't have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this issue is easily fixed, and can reduce quite a few incidents of back discomfort.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. They are low-priced, frequently being below twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most widespread condition impacting people today. Over 80 million men and women are affected by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses millions of dollars year after year on account of lost time and production. Innovative and more effective treatment solutions are continually sought after in the hope of lowering economic influence this condition causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these cases Shoe Lifts might be of beneficial. The lifts are capable of eliminating any discomfort and pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic doctors.
So as to support the human body in a well-balanced fashion, your feet have got a critical part to play. Despite that, it is sometimes the most overlooked zone of the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This causes other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that the right posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this issue is easily fixed, and can reduce quite a few incidents of back discomfort.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. They are low-priced, frequently being below twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most widespread condition impacting people today. Over 80 million men and women are affected by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses millions of dollars year after year on account of lost time and production. Innovative and more effective treatment solutions are continually sought after in the hope of lowering economic influence this condition causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these cases Shoe Lifts might be of beneficial. The lifts are capable of eliminating any discomfort and pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic doctors.
So as to support the human body in a well-balanced fashion, your feet have got a critical part to play. Despite that, it is sometimes the most overlooked zone of the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This causes other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that the right posture and balance are restored.
What Can Cause Inferior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
The plantar fascia is connective tissue on the sole of your foot. When the arch of the foot is not properly supported, the plantar fascia can stretch and pull away from the heel area. When the plantar fascia pulls away from the heel, calcium deposits form in its absence. These calcium deposits are called heel spurs and can be very painful.
Causes
A strong band of sinew (plantar fascia) stretches across the sole of the foot below the surface of the skin and is attached to a point in the middle of the under surface of the heel bone. With repeated activity on our feet, the plantar fascia can become tight and cause persistent traction (tugging) on its attachment point into the heel bone, and inflammation and pain may develop at this site. This painful condition is known as plantar fasciitis. Sometimes a ?spur? develops at the site of this traction on the bone and protrudes into the surrounding tissue. This is a heel spur.

Symptoms
Symptoms of heel spur syndrome often include pain early in the morning or after rest, as you take the first few steps. It may also include severe pain after standing or walking long hours, especially on hard cement floors. Usually more pain exist while wearing a very flat soled shoe. A higher heel may actually relieve the pain as an arch is created. The pain is usually sharp, but can also be a dull ache. The pain may only be at the bottom of the heel, or may also travel along the arch of the foot.
Diagnosis
A heel spur is often seen on X-ray as a bony protrusion, which can vary in size. However, because a Heel Spur only indicates increased load on the plantar fascia, and not pain, an ultra sound may be required to assess other actual cause of the heel pain such and may include checking to see if the plantar fascia is inflamed or degenerated.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key for the proper treatment of heel spurs is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation, and allow the condition to heal. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, losing weight, wearing shoes that have a cushioned heel that absorbs shock, and elevating the heel with the use of a heel cradle, heel cup, or orthotic. Heel cradles and heel cups provide extra comfort and cushion to the heel, and reduce the amount of shock and shear forces experienced from everyday activities.
Surgical Treatment
Usually, heel spurs are curable with conservative treatment. If not, heel spurs are curable with surgery, although there is the possibility of them growing back. About 10% of those who continue to see a physician for plantar fascitis have it for more than a year. If there is limited success after approximately one year of conservative treatment, patients are often advised to have surgery.
Prevention
There are heel spur prevention methods available in order to prevent the formation of a heel spur. First, proper footwear is imperative. Old shoes or those that do not fit properly fail to absorb pressure and provide the necessary support. Shoes should provide ample cushioning through the heel and the ball of the foot, while also supporting the arch. Wearing an orthotic shoe insert is one of the best ways to stretch the plantar fascia and prevent conditions such as heel spurs. Stretching the foot and calf is also helpful in preventing damage. Athletes in particular should make sure to stretch prior to any physical activity. Stretching helps prevent heel spurs by making tissue stronger as well as more flexible. In addition, easing into a new or increasingly difficult routine should be done to help avoid strain on the heel and surrounding tissue.
Preventing Posterior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Bone spurs usually form around joints that have arthritis, in the vertebrae of the spine, and on the heel. When they form on the heel, they may form on the back of the heel but usually form on the bottom of the heel. Of course, this is where all of the body weight comes down with each step. Spurs on the bottom of the heel are usually most painful the first few steps out of bed each morning. The pain may lessen somewhat after walking for a few minutes, but may be intense again after sitting for a half hour or so, such as after lunch. The pain usually gets worse throughout the day as you are up on your feet more. Often the pain feels like a nail being driven through the heel into the ankle and leg.
Causes
Faulty foot structures such as abnormal growths, different leg lengths, and unhealed injuries and haveinf flat feet or high arches. Muscle imbalances tight, weak or shortened muscles in your foot, plantar fascia, ankle, calf and hamstring. Over pronation can cause imbalance in foot mechanics which puts excess pressure on the plantar fascia. Poor biomechanics affect the way your foot hits the ground. If you overpronate (feet roll inward) you tend to have flat feet (pes planus), which increases stress on the heel bone. Regular shoes or high heels that are too tight or don't support your heel or arch affect the distribution of your body weight on your foot. Health conditions such as obesity, inflammatory diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis), bursitis, neuroma (nerve growths), gout, diabetes, Haglund's deformity, and Achilles tendinitis can also instigate the problem. Running or jogging on hard surfaces, repetative striking of the heel bone.

Symptoms
Although it may take years to become a problem, once it appears, it may cause considerable suffering. Because of proximity to the tendons, the spur is a source of continuous painful aching. The sensation has been described as "a toothache in the foot." When you place your weight on the heel, the pain can be sufficient to immobilize you.
Diagnosis
A thorough medical history and physical exam by a physician is always necessary for the proper diagnosis of heel spurs and other foot conditions. X rays of the heel area are helpful, as excess bone production will be visible.
Non Surgical Treatment
To aid in the reduction of inflammation, applying ice for 10-15 minutes after activities and the use of anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, can be helpful. Corticosteroid injections may also be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy can be beneficial with the use of heat modalities, such as ultrasound, that create a deep heat and reduce inflammation. If the pain caused by inflammation is constant, keeping the foot raised above the heart and/or compressed by wrapping with a bandage will help. Taping can help speed the healing process by protecting the fascia from reinjury, especially during stretching and walking.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery involves releasing a part of the plantar fascia from its insertion in the heel bone, as well as removing the spur. Many times during the procedure, pinched nerves (neuromas), adding to the pain, are found and removed. Often, an inflamed sac of fluid call an accessory or adventitious bursa is found under the heel spur, and it is removed as well. Postoperative recovery is usually a slipper cast and minimal weight bearing for a period of 3-4 weeks. On some occasions, a removable short-leg walking boot is used or a below knee cast applied.
Prevention
There are heel spur prevention methods available in order to prevent the formation of a heel spur. First, proper footwear is imperative. Old shoes or those that do not fit properly fail to absorb pressure and provide the necessary support. Shoes should provide ample cushioning through the heel and the ball of the foot, while also supporting the arch. Wearing an orthotic shoe insert is one of the best ways to stretch the plantar fascia and prevent conditions such as heel spurs. Stretching the foot and calf is also helpful in preventing damage. Athletes in particular should make sure to stretch prior to any physical activity. Stretching helps prevent heel spurs by making tissue stronger as well as more flexible. In addition, easing into a new or increasingly difficult routine should be done to help avoid strain on the heel and surrounding tissue.